
What are problems caused by photochemical smog? How does classical smog different from photochemical smog? Which city is famous for its photochemical smog? Photochemical smog is capable of inflicting irreversible damage on.

People with pre-existing health problems (such as respiratory diseases). Effects on Environment. The toxic chemicals formed in a photochemical smog can irritate nasal passages and eyes.
Breathing problems can become aggravated due to prolonged exposure to smog conditions. Some of the toxins created by chemical reactions in the photochemical smog are carcinogenic. When combined with hydrocarbons, the chemicals contained within it form molecules that cause eye irritation. Radicals in the air interfere with the nitrogen cycle by preventing the destruction of ground level ozone. Other effects include reduced visibility and respiratory ailments.
The effects include: Coughing and irritation of the eyes, chest,. Summer smog is also known as photochemical smog. Ozone , a colorless, odorless gas, can be good when in the upper atmosphere but harmful when found near ground level. Respiratory problems are caused by the pollutants being breathed in,. Steps taken towards decreasing smog.
This is because the photochemical reactions that cause smog to take place in the air when the released pollutants from heavy traffic drift due to the wind. Smog can thus affect and prove to be dangerous for suburbs, rural areas as well as urban areas or large cities. For example, photochemical smog is a typical form of pollution of all the main urban and industrial areas of the world. It occurs in or near areas with a high traffic density and in the presence of specific climatic conditions (no wind or weak winds, high temperatures, etc.) that cause the concentration of polluting gases to increase.
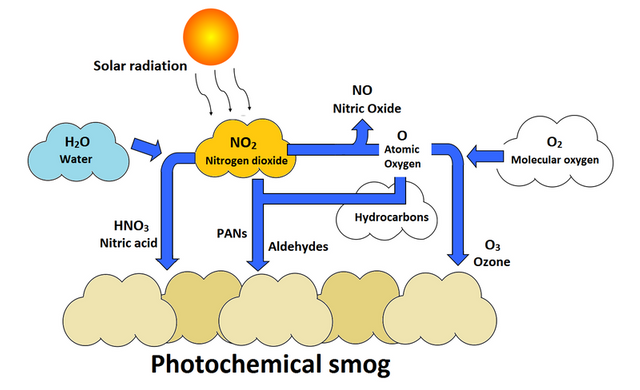
Smog contains soot particulates like smoke, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and other components. At least two distinct types of smog are recognized:. The main visible effect is the brown haze that can be seen above many cities. The brown tinge is caused by very small liquid and solid particles scattering the light.
These effects are worse when the sun is highest because the pollutants react with it. It is a condition that develops when oxides of nitrogen and VOCs (volatile organic compounds) interact in the presence of sunlight to produce a mixture of hundreds of hazardous chemicals,. Smog is a byproduct of modern industrialization. Smog can cause or aggravate health problems such as asthma, emphysema, chronic bronchitis and other respiratory problems as well as eye irritation and reduced resistance to colds and lung infections. Swann HE, Jr, Balchum OJ.
Biological effects of urban air pollution. Chronic exposure of guinea pigs. Furthermore, this smog depends on the primary pollutants and also on the formation of secondary pollutants. This smog is visible as a brown haze. This demonstration is basically looking at how ozone forms or how photochemical smog forms at the ground level because of the pollutants that we emit.
Ozone emission or ozone formation depends on two ingredients, nitrogen oxides that are emitted by pollutants that are going out to the tail pipe of a car and in a power plant with a stack. These emissions combine in the presence of sunlight to create a noxious environment, which can be harmful to human health. These secondary oxidants and acids play important roles in the effects of smog on ecosystems and human health, as well as in agriculture and materials damage on urban, regional, and global scales.
In humans, the most severe effects of smog is experienced by the aged people, children and those who are already suffering from respiratory illnesses like asthma and bronchitis. Smog allows the toxic gases like carbon monoxide, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide to remain suspended close to the groun. Sulfurous smog, which is also called “London smog,” from a high concentration of sulfur oxides in the air and is caused by the use of sulfur-bearing fossil fuels, particularly coal.
This type of smog is aggravated by dampness and a high concentration of suspended particulate matter in the air.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.