
How does nitrogen dioxide get into the air? What causes nitrogen oxide? NO primarily gets in the air from the burning of fuel. NO forms from emissions from cars, trucks and buses, power plants, and off-road equipment. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO ) is one of a group of gases called nitrogen oxides (NO x).
Other nitrogen oxides include nitrous acid and nitric acid. Its presence in air contributes to the formation and modification of other air pollutants , such as ozone and particulate matter, and to acid rain. Nitrogen oxides are produced by human activity of the time, and produced naturally the other during thunderstorms by electric discharge.
NOforms when fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gas or diesel are burned at high temperatures. NOand other nitrogen oxides in the outdoor air contribute. NO x pollution occurs when nitrogen oxides are released as a gas into the atmosphere during the high-temperature combustion of fossil fuels.
The law also requires EPA to periodically review the standards and revise them if appropriate to ensure that they provide the requisite amount of health and environmental protection and to update those standards as necessary. The two most prevalent oxides of nitrogen are nitrogen dioxide (NO 2) and nitric oxide (NO). Both are toxic gases with NO being a highly reactive oxidant and corrosive.
The major source of nitrogen dioxide in Australia is the burning of fossil fuels: coal, oil and gas. It is one of several nitrogen oxides. It has a significant impact on human health, contributing particularly to.

It can cause significant health issues by irritating the lungs and can contribute to respiratory problems. Coal- and gas-fired power plants and vehicles constitute the major anthropogenic (human-produced) sources. Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula NO 2. These gases, especially nitrogen dioxide , are products of vehicle, power plant, and off-road equipment emissions caused by fuels burning at high heat. Nitrous oxide emissions gets produced by both natural and human sources.
This site provides information about nitrogen dioxide and its effects. For standards-setting, EPA uses nitrogen dioxide (NO ) as an “indicator pollutant,” meaning, if nitrogen dioxide pollution exists in the air, so do other nitrogen oxides. The sum of nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO 2) is commonly called nitrogen oxides (NO x ). Other compounds, including nitrous acid and nitric aci are part of the NO x family. NO is the component of greatest interest and the indicator for the larger group of NO x. There are seven oxides of nitrogen that may be found in the ambient air.
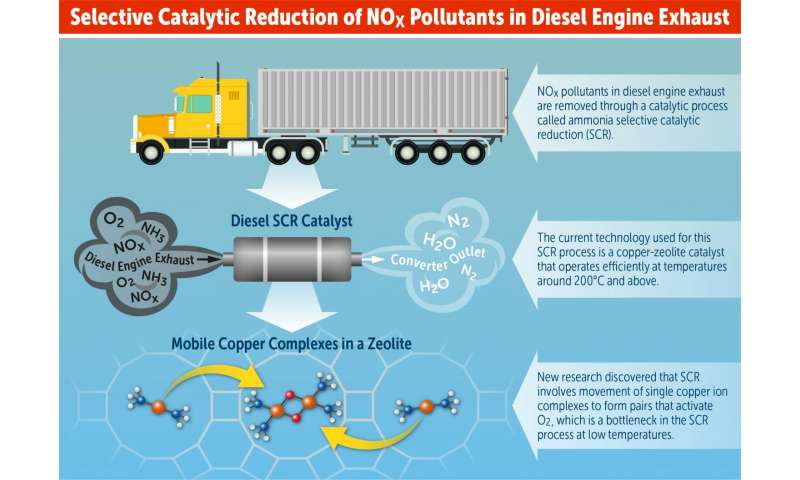
However, nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) are the two principal nitrogen oxides associated with combustion sources. Road traffic is a leading source. Airborne nitrogen pollution affects not only the quality of the air we breathe, but also the land and the water. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the air and is essential to plant and animal life. Sentinel-5P is the umpteenth spacecraft belonging the the Sentinels constellations and conceived in the framework of the Copernicus Programme.
Mapped: nitrogen dioxide pollution around the world. From cities in Europe to wildfires in Africa, data from a new European Space Agency satellite reveals the scale and spread of NOon a global scale. Is NO per se responsible for effects on health? Environmental Effects: Nitrogen oxides help form acid rain.
In addition, this pollutant can cause a wide range of environmental damage, including visibility impairment and eutrophication - that is, explosive algae growth which can deplete oxygen in water bodies such as the Chesapeake Bay. They contribute to air pollution and can be harmful to human health. These nitrogen oxides contribute to the problem of air pollution , playing roles in the formation of both smog and acid rain. Nitrogen oxides are critical components of photochemical smog.
They produce the yellowish-brown colour of the smog. Nitric oxide is colourless and is oxidised in the atmosphere to form nitrogen dioxide.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.