How to stop ozone depletion? What are the dangers of O3? How stratospheric ozone is made? Inhaling ozone can cause coughing, shortness of breath, worse asthma or bronchitis symptoms, and irritation and damage to airways. EPA regulations help states reduce ozone levels in outdoor air.
Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen ( O). You can reduce your exposure to ozone pollution by checking air quality where you live. It is unstable and highly reactive.
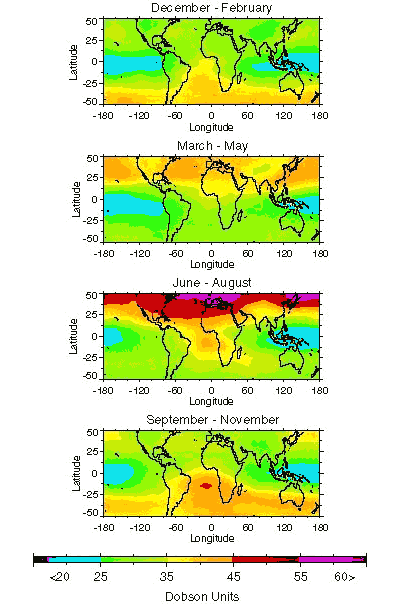
Ozone can be good or ba depending on where it is found. High up in the atmosphere, ozone forms a layer that shields the Earth from ultraviolet rays. At low concentrations, it is toxic. However, at ground level, ozone is considered a major air pollutant.
At ground level, however, ozone is bad news, because it is highly corrosive, and it can damage the respiratory tract when inhaled and injure the vascular systems of plants, causing damage or death. Ozone ( O) is a highly reactive gas composed of three oxygen atoms. Ozone at ground level is a harmful air pollutant.
In another study, house dust mite (HDM) sensitive individuals underwent airway challenge with HDM antigen after ozone exposure and after air exposure. As seen in Figure 1 after ozone exposure , the concentration of HDM needed to cause a fall in FEVwas reduced compared to the air exposure,. Often called smog, ozone is harmful to breathe. When ozone is present, there are other harmful pollutants created by the same processes that make ozone.
Ozone aggressively attacks lung tissue by reacting chemically with it. So far we have emphasized the beneficial nature of tropospheric Oas the precursor of OH. In surface air, however, Ois toxic to humans and vegetation because it oxidizes biological tissue. But closer to earth, ozone is an air pollutant that can be harmful to humans. When ground level ozone is create it hangs around in the layer of air near the ground.
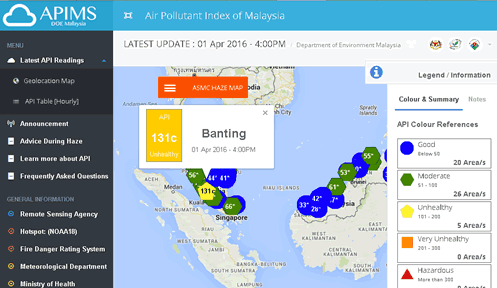
However, ozone (O ) pollution was found to steadily deteriorate in most part of eastern China, especially in developed regions such as Jing-Jin-Ji (JJJ), Yangtze River Delta region (YRD) and Pearl River Delta region (PRD). See fact sheet on air toxics. The AQI measures concentrations of five air pollutants: ozone, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide. The EPA has chosen these pollutants as criteria pollutants, but these are not all of the pollutants in the air.
These concentrations are compared to a standard set out in federal law. O) Colorless (or faintly blue), unstable (reactive), and water soluble gas having chlorine-like odor, and formed in the upper atmosphere by the action of solar radiation on oxygen. VOCs are emitted by a variety of sources, including motor vehicles, chemical plants, refineries, and other factories. NOx is emitted by motor vehicles, electric power plants, and other combustion sources.
Ground-level ozone (O ) is regulated by EPA. Ozone pollution can even come from paints, cleaners, solvents, and motorized lawn equipment. The ozone molecule (O ) is harmful to air quality, outside of the ozone layer. Others include carbon monoxide, lea nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide, as well as scores of toxins such as mercury, arsenic, benzene, formaldehyde and acid gases. Ozone, O is composed of three oxygen atoms joined together.
Two oxygen atoms joined together form the basic oxygen molecule O2. The additional third atom makes ozone an unstable, highly reactive gas. Evidence of the health effects of air pollution at levels currently common in Europe has grown stronger over the past few years, and is sufficient to recommend further policy action to reduce emissions of particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide. Air Quality Guide for Ozone.
Use the chart below to help reduce your exposure and protect your health. Air pollution is perceived as a modern-day curse: a by-product of increasing urbanization and industrialization. It does, however, have a long and evolving history with interesting transitions in line with economic, technological and political change.
Emissions from the above sources in the winter in the San Joaquin Valley do not typically produce high ozone levels due to diminished sunlight and cooler temperatures. Unhealthy ozone levels occur when precursor emissions react in the presence of sunlight, warm temperatures and light winds. Ozone forms when two types of pollutants (VOCs and NOx) react in sunlight. These pollutants come from sources such as vehicles, industries, power plants, and products such as solvents and paints.
Air pollution – the combination of outdoor and indoor particulate matter, and ozone – is a risk factor for many of the leading causes of death including heart disease, stroke, lower respiratory infections, lung cancer, diabetes and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.