What are four examples of air pollutants? The Clean Air Act requires EPA to set National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) National Ambient Air Quality StandardsNational Ambient Air Quality Standards established by EPA for six criteria pollutants in outdoor air. NAAQS are currently set for carbon monoxide, lea ground-level ozone, nitrogen dioxide, particulate matter, and sulfur. Sections 1and 1of the Clean Air Act (CAA) govern the. Particulate matter (PM) is one of the air pollutants.
CAPs are typically emitted from many sources in industry, mining, transportation, electricity generation and agriculture. These pollutants were selected from the six criteria pollutants and from the 1toxic air pollutants on the basis of their prevalence in the United States, their physicochemical behavior, and the magnitude of their potential health threat. These commonly found air pollutants (also known as criteria air pollutants) are found all over the United States.
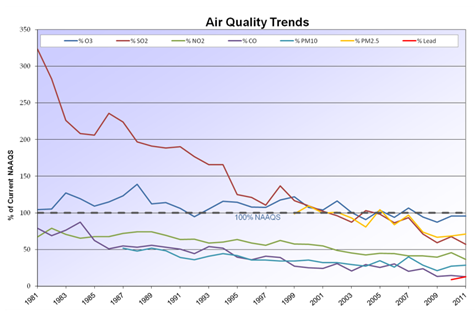
The criteria air pollutants include particle pollution, ground-level ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen. Under the federal Clean Air Act, the U. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established health- and science-based National Ambient Air. The information gathered is used to help determine if our local air quality attains the federal health-based NAAQS, as shown below. Visit the Air Quality Monitoring website to access current criteria pollutant data.
The Air District prepares emissions inventories of these criteria pollutants (except lead emissions, which are included in the toxic air contaminant reporting process). The six criteria air pollutants regulated by the EPA include particulate pollution, ground-level ozone, lea carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. Our efforts to reduce carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and lead in our air continue, although levels of these pollutants are now well below federal air quality standards.
Criteria Pollutant Emissions Inventory. The air contains a vast range of other gasses and particles in much smaller quantities. Some of these, known as air pollutants , can impact human health and the environment. Some air pollutants come from natural sources, such as forest fires, lightning, and plants.

The Clean Air Act requires the US EPA to set National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for six common air pollutants , called “ criteria pollutants ”, to protect health, the environment, and property. Sources and Effects of Common Air Pollutants. Air pollution is a growing problem around the worl with individuals and nations alike pumping enormous volumes of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere every day. These pollutants are not only dangerous to the health and wellbeing of plants, animals, and people, but they are also a major.
The EPA developed National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for these pollutants to protect public health and the environment. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The six commonly found air pollutants , which are also known as “ criteria pollutants ,” are found all over the United States, which is one of many aspects of.
Air pollutants are responsible for a wide range of adverse health and environmental effects. Both criteria pollutants and toxic air contaminants are measured statewide to assess the adequacy of programs for cleaning the air. CARB works with local air pollution control districts to reduce air pollution from all sources.
The table below briefly summarizes the most common health and environmental effects for each of the air pollutants for. Based on NAAQS dropdown selection, a synchronized set of charts ( air quality concentration chart, emissions stacked area chart and USA map of monitor locations) display. General information on the six criteria pollutants and associated TCEQ planning activities.
One key feature of criteria air pollutants is that they are generally widely distributed.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.